Unreal Birth Circumstances – Jesus of Nazareth
Opening the Nativity story were activities in Rome, Persia and Nazareth, hundred miles apart from each other. Incredibly, after months in the making, the confluence of events culminated in a small town where none of them lived.
Gospel accounts of Matthew and Luke cover the Nativity story, each complimenting the other with few overlapping details. According to Luke, Caesar Augustus issued a registration decree although the Roman story behind the story is not told.

On February 5, 2 BC, the Roman Senate designated Caesar Augustus as the Pater Patrie, Father of the County. In The Deeds of Divine Augustus, the honor was listed as one the 35 accomplishments of his 25 years of rule.[1]
To honor Augustus in 2 BC, planning began for a special registration of the entire Roman Empire including the provinces, not the typical census for citizens of Rome. Each registrant was expected to swear an oath of allegiance to Augustus.[2]
Logistics to execute this registration decree required considerable planning, time and resources, especially in a era without electricity, computers, phones, etc. For town criers, praeco in Latin, to announce the decree in far reaching locations of the Empire would take months.[3]
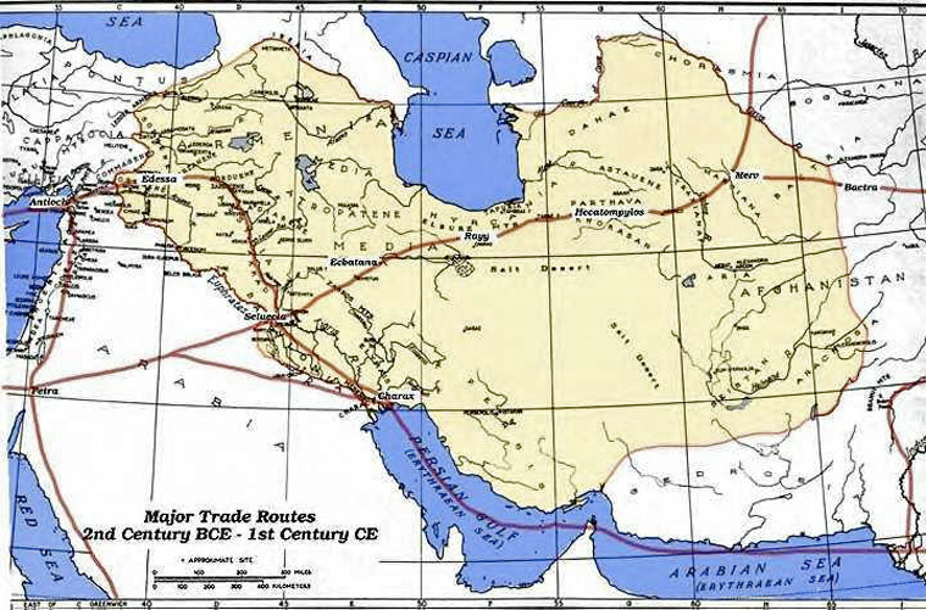
Meanwhile, Magi “from the East” (Persia, by reputation and historical context), according to Matthew, saw stellar and planetary alignments signaling something exceptional was about to happen – the birth of a King of Judea. Not just any King – what they saw was so awe-inspiring, they were moved to act.
Believing wholeheartedly in their observations, they planned a journey that would cover hundreds of miles by camel in a quest to find this special baby King. Much more than just a tribute visit, they intended to present the baby with expensive precious gifts and worship him.
Greek text of Matthew uses the word proskynēsai or proskuneo translated as “worship.” Meaning of the word is “to do reverence to;” “bow down or bow down before;” “kneeling or prostration to do homage (to one).”[4]
Not knowing their final destination, the Magi initially headed for Jerusalem, the government center of Judea. It seemed to be a good place to get information and traveled to the palace of Judea’s King Herod to ask him.
In another concurrent series of events while the Magi were on their journey to Jerusalem, Joseph and Mary were busy going about their daily business. Preparing for the arrival of their new baby, they were planning his birth in Nazareth without any clue what was about to befall them.
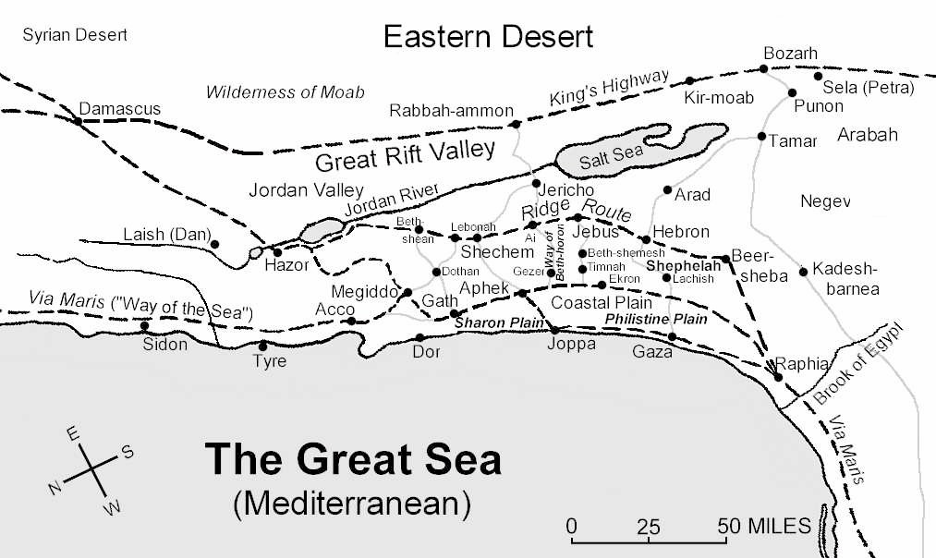
Suddenly, everything changed – a praeco announced Augustus’ registration decree compelling the betrothed couple to do the unthinkable. On short notice, they had to embark on an unplanned, 90-mile trek on foot to register in Bethlehem to comply with the decree in-spite-of Mary’s imminent childbirth.
No one or thing trumped a decree by a Roman Caesar and although it is not definitively stated that the decree had a deadline, Rome expected prompt compliance. Evidence of this urgency is seen by the immediate response of Joseph and Mary.
People were required to register in the home town of their family linage. In the case of Joseph and Mary, it was Bethlehem, the home town of King David who lived about a 1000 years earlier.
No doubt Mary would give birth before they returned to Nazareth where Mary should have been with her family and friends. If the praeco had announced the decree about two weeks earlier or later, Jesus would not have been born in Bethlehem.
Weary from the unplanned long trip from Nazareth, Joseph and Mary discovered lodging accommodations in Bethlehem were full and they had to stay in a stable. As if this situation wasn’t challenging enough, Mary went into labor in the stable and was forced to give birth to Jesus using a manger for his crib.
According to Luke, the birth of Jesus was heralded by a host of angels. Shepherds left their flocks in the fields and went to Bethlehem to see this sight.
Arrival in Jerusalem by the Magi entourage was big news since it was not often that Magi visited the city being off the major trade routes…and it likely caused a stir. Judaism shunned the mystic practices of the Magi even though they were favored by the Herod.
King Herod immediately granted the Magi access to his palace when the they arrived. Magi informed him of a new King of Judea, one with his own star – it was most shocking news to the reigning King.
At that point, Herod did not know any further details and dismissed the Magi. However, it can be surmised the King believed that the Magi knew something profound, both considering their reputation and the fact of their long journey to honor and worship this baby.
Herod summonsed the Jewish chief priests and scribes and asked if they knew where Christos was to be born. No ambiguity surrounded the question, the Jewish religion experts knew exactly what Herod was asking.
An ancient prophecy from the Jewish prophet Micah foretold the Messiah was to be born in “Bethlehem in land of Judah.” Herod believed the prophecy as evidenced by his next actions.
Planning to exchange this prophetic knowledge to learn the exact location of the baby, Herod secretly called the Magi to return back to the palace. The Magi unwittingly agreed to the deal.
After leaving Herod’s palace, “his Star” reappeared at some point to the Magi and it shone over Bethlehem corroborating the information. Still not exactly sure of their final destination, they headed South toward Bethlehem just a short distance away.
Far off the path of a major trade route, unexpectedly the Magi from Persia arrived in Bethlehem. If their arrival was big news in Jerusalem, image what it was in the much smaller hamlet.
Everyone knows everyone else’s business in a small town so finding the child would not have been difficult. Magi found the new family, then presented the newborn with their precious gifts and worshiped him.
Not all the drama was finished. Warned in a dream, according to Matthew, the Magi did not return to Jerusalem to tell Herod where the Christos was located.
Once Herod realized he had been duped, he commanded that all the male babies in the Bethlehem area under 2 years of age to be killed. Actions taken by the King were consistent with his ruthless reputation, but the new family escaped by hiding in Egypt until Herod died shortly thereafter.
Was it just a coincidence that the confluence of these 3 events culminated in Bethlehem … or was it a divine plan?
Updated July 5, 2025.
REFERENCES:
[1] Augustus, Caesar. The Deeds of the Devine Augustus. Trans. Thomas Bushnell. The Internet Classics Archive. Ed. Daniel C. Stevenson. MIT Program in Writing and Humanistic Studies. 2009. <http://classics.mit.edu/Augustus/deeds.html> “Res Gestae Divi Augusti” “The Achievements of the Divine Augustus.” Skidmore.Edu. Trans. P. A. Brunt and J. M. Moore. pp 2-8.<//mail.classics.domains.skidmore.edu/cw/readings-campus-only/Res%20Gestae.pdf>
[2] Martin, Ernest L. The Star of Bethlehem – The Star That Astonished the World. Associates for Scriptural Knowledge. 2003. “The Census of Quirinius.” <https://www.askelm.com/star/star006.htm. “Roman census oath” AI search. Yahoo.com. <https://search.yahoo.com/yhs/search?hspart=adk&hsimp=yhs-adk_sbnt¶m1=20210118¶m2=00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000¶m3=searchmanager_%7EUS%7Eappfocus1%7E¶m4=%7Efirefox%7E%7E&type=yhs-adk_sbnt_appfocus1_sm_ff&grd=1&p=Roman+census+oath> Smallwood, E. Mary. The Jews Under Roman Rule: From Pompey to Diocletian. 2nd Ed. 1981. <http://books.google.com/books?id=jSYbpitEjggC&lpg=PA151&ots=VWqUOinty4&dq=census%20Syria%20Rome&pg=PP1#v=onepage&q&f=false>
[3] “What does praeco mean in Latin?” WordHippo.com. <https://www.wordhippo.com/what-is/the-meaning-of/latin-word-abe157d29d6f84e34e7ea3e1aedf4327661a704c.html> “praeco, praeconis [m.] C.” Latin-Is-Simple.com. n.d. <https://www.latin-is-simple.com/en/vocabulary/noun/13962/> Last accessed 5 July 2025.
[4] Matthew 2:2 BibleHub.com. Lexicon. <https://biblehub.com/lexicon/matthew/2-2.htm>