Mount Moriah – the Connection
Mount Moriah is first mentioned in the Bible in Genesis going back to the days of Abraham when it first gained importance as a sacred site.[1] By birth a Chaldean, Abraham followed God’s instruction to leave for an unknown land along with a blessing.[2]
Abraham eventually settled in Canaan at Hebron about 20 miles south of the mounts of Moriah and Salem.[3] One day, God tested Abraham’s faith by instructing him to offer Isaac, his only son with his wife Sarah, as a sacrifice in “the land of Moriah…on one of the mountains that I shall show you.”[4]
Human sacrifices were not uncommon in that era, such as to the pagan gods Baal and Moloch.[5] Faithfully Abraham built an altar on God’s chosen Moriah mount and was in the act of offering Isaac as a sacrifice when an “angel of the Lord” stopped him and provided a substitute sacrifice, a ram stuck in a thicket.
Known as “The Binding of Isaac” in Jewish tradition, the story in Genesis is read on the first day of Rosh Hashanah, the Jewish New Year.[6] God promised Abraham’s name would be great, the father of a great nation in whom all the families of the earth would be blessed.
Moriah means “chosen by Jehovah,” albeit Abraham was so moved by the experience with his only son, he called this particular Mount of Moriah, hwhy har or Y@hovah ra’ah meaning “the LORD will Provide.”[7] Some Bibles translate the Hebrew name it as Jehovahjireh.
“The Lord will choose and see for Himself this place, to cause His Divine Presence to rest therein and for offering sacrifices here…that [future] generations will say about it, ‘On this mountain, the Holy One, blessed be He, appears to His people.’” – Rabbi Rashi [8]
Several hundred years later, soon after the Exodus from Egypt, the Hebrew nation encamped at Mount Sinai. God handed down the Law to Moses which included prophetic promises about the place hinting that the land of Moriah was part of God’s future master plan.
One promise was that God would lead Israel to the land sworn to Abraham, Isaac and Jacob. God also promised He would provide a permanent place for His Name to dwell.[9]
In the land of Abraham, King David established his throne in the city of Jerusalem encompassing Mount Moriah. A most unusual set of circumstances brought the Mount to center stage.[10]
King David angered God due to his lack of faith by conducting a census leading to a severe judgement on his kingdom of Israel. Taking responsibility, David pleaded with God to stop the judgement on the people because it was his own sin, not theirs.
Executing and halting the judgment was an angel visible only to the King. God instructed David, through the prophet Gad, to offer an atonement sacrifice for the people of Israel.[11]
Preparing for the sacrifice, David bought the threshing floor of Araunah (Ornan) located on Mount Moriah primarily because of its high location.[12] The King also bought Araunah’s oxen and equipment.[13]
On Mount Moriah David built the altar using the wood as fuel for the altar’s fire and slew the oxen for the offering. Something miraculous then happened – fire came down from heaven and consumed the sacrifice deeply affecting David who proclaimed:[14]
I Ch. 22:1 “This is the place where the temple of the Lord God will be, along with the altar for burnt sacrifices for Israel.”(NET)
God informed the King that his son would build the House of God, not him.[15] After David’s death, in the fourth year of King Solomon’s reign, the building of the Temple commenced on Mount Moriah:
2 CH 3:1 Then Solomon began to build the house of the LORD in Jerusalem on Mount Moriah, where the LORD had appeared to his father David, at the place that David had prepared on the threshing floor of Ornan the Jebusite. (NASB)
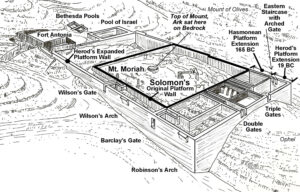
Seven years later the Temple was completed.[16] To commemorate the occasion, Solomon held a public consecration and blessing acknowledging the fulfillment of God’s promises:
2 CH 6:2, 4 “I have surely built You an exalted house, and a place for You to dwell in forever.” … “Blessed be the LORD God of Israel, who has fulfilled with His hands what He spoke with His mouth to my father David, saying,
2 CH 6:5-6 “‘Since the day that I brought My people out of the land of Egypt, I have chosen no city from any tribe of Israel in which to build a house, that My name might be there, nor did I choose any man to be a ruler over My people Israel. Yet I have chosen Jerusalem, that My name may be there; and I have chosen David to be over My people Israel.’(NKJV)
In spectacular fashion, that day on Mount Moriah God once again sent fire down from heaven to consume the first sacrifices offered at the new Temple. The celebration continued for seven days with the completion of the Temple.
A thousand years later on the sacred Mount Moriah, Jesus of Nazareth stood trial before the Priests and Scribes of the Temple, the House of God, and declared himself to be the Son of God. Perceived as a blasphemy, it triggered a string of events in the following hours leading to the crucifixion of Jesus on the first day of the Passover.
United States Federal legal definition of the Doctrine of Chances is the premise for the obvious question: What is the probability of chance that the location, the timing, and the circumstances of the crucifixion of Jesus of Nazareth were all an accident?
Updated April 20, 2025.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
REFERENCES:
[1] “Abraham.” Jewish Virtual Library. 2018. <https://www.jewishvirtuallibrary.org/abraham>
[2] Genesis 12.
[3] Genesis 11-15. “Hebron.” Bible-History.com. 2017. <http://www.bible-history.com/geography/ancient-israel/hebron.html>
[4] NRSV.
[5] Genesis 22. Quote – all mainstream Christian and Jewish Bible translations. Josephus, Flavius. Antiquities of the Jews. Book I, Chapter XIII. The Complete Works of Josephus. Trans. and commentary. William Whitson. <http://books.google.com/books?id=e0dAAAAAMAAJ&printsec=frontcover&source=gbs_ge_summary_r&cad=0#v=onepage&q&f=false>
[6] Genesis 22. “The Binding of Isaac.” My Jewish Learning. 2018. <https://www.myjewishlearning.com/article/the-binding-of-isaac> “The Great Test: The Binding of Isaac.” Chabad.org. 2018. <https://www.chabad.org/library/article_cdo/aid/246616/jewish/The-Great-Test-The-Binding-of-Isaac.htm> “Human Sacrifices.” Bible-history.com. n.d. <http://www.bible-history.com/backd2/human_sacrifice.html> Hefner, Alan G. “Baal.” Encyclopedia Mythica. 2004. <http://www.pantheon.org/articles/b/baal.html> “Sacrifice.” Jewish Encyclopedia.
[7] Net.bible.org. Genesis 22:2, Hebrew text Mowriyah <04179>; Genesis 22:14, Hebrew text “ra’ah <07200>;” Y@hovah <03068>;” “Y@hovah yireh <03070>”
[8] Rashi, Shlomo Yitzchaki. The Complete Jewish Bible with Rashi Commentary. Bereishit – Genesis 22:14 commentary. <https://www.chabad.org/library/bible_cdo/aid/8217#showrashi=true>
[9] I Chronicles 17.
[10] I Chronicles 17; 2 Samuel 5, 7. Josephus. Antiquities. Book VII, Chapter III.
[11] II Chronicles 3.
[12] I Chronicles 21; 2 Chronicles 3; 2 Samuel 24. Josephus. Antiquities. Book VII, Chapter III. “Herod’s Temple.” Bible-History.com. 2017. <http://www.bible-history.com/jewishtemple/JEWISH_TEMPLEThe_Site.htm>
[13] I Chronicles 21; 2 Samuel 24.
[14] 2 Samuel 24; 1 Chronicles 21.
[15] I Chronicles 22, 28.
[16] 1 Kings 6; 2 Chronicles 3. Wiemers, Galyn. Generation Word. “Chapter 21 – Solomon’s Temple Mount.” image. 2018. <https://www.generationword.com/devotions/photos-diagrams/diagrams/oct-digrams/29a-solomons-temple-mount-retaining-wall-2500-jpg.jpg>
 Three of David’s brothers were fighting in Israel’s army supported by their father who routinely sent David to them with supplies. During one visit, David was astonished to see Israel’s army afraid of an ace giant Philistine warrior named Goliath who challenged and taunted Israel’s army daily.
Three of David’s brothers were fighting in Israel’s army supported by their father who routinely sent David to them with supplies. During one visit, David was astonished to see Israel’s army afraid of an ace giant Philistine warrior named Goliath who challenged and taunted Israel’s army daily. Uriah was summoned from the battlefield at the behest of David under the pretense of earning a well-deserved leave from duty. The true reason was to give Bath-Sheba an opportunity to have marital relations with her husband to legitimize her pregnancy.
Uriah was summoned from the battlefield at the behest of David under the pretense of earning a well-deserved leave from duty. The true reason was to give Bath-Sheba an opportunity to have marital relations with her husband to legitimize her pregnancy. Israel conquered its enemies in the land and each of the 12 tribes of the sons of Israel were allotted their own regions.
Israel conquered its enemies in the land and each of the 12 tribes of the sons of Israel were allotted their own regions.